
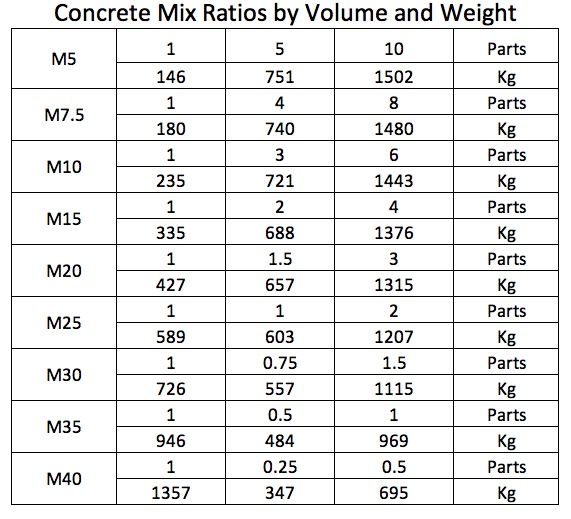
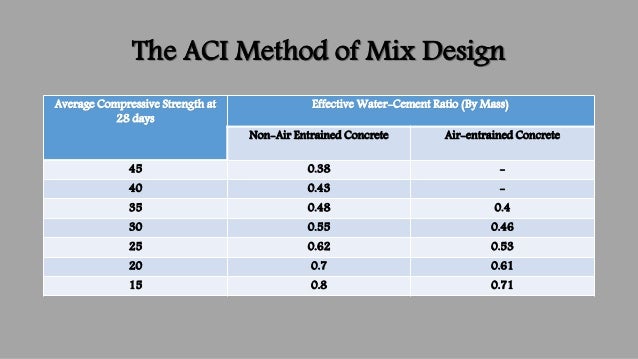
High strength concrete mixtures generally need to have a low water-cementitious materials ratio (w/ cm).Most mixtures contain one or more supplementary cementitious materials such as fly ash (Class C or F), ground granulated blast furnace slag, silica fume, metakaolin or natural pozzolanic materials. High strength concrete mixtures will have a high cementitious materials content that increases the heat of hydration and possibly higher shrinkage leading to the potential for cracking.The sand may have to be coarser than that permitted by ASTM C 33 (fineness modulus greater that 3.2) because of the high fines content from the cementitious materials. Generally smaller maximum size coarse aggregate is used for higher strength concretes. They need not necessarily be hard and of high strength but need to be compatible, in terms of stiffness and strength, with the cement paste. Aggregates should be strong and durable.Some of the basic concepts that need to be understood for high strength concrete are:
Optimum concrete mixture design results from selecting locally available materials that make the fresh concrete placeable and finishable and that ensure the strength development and other desired properties of hardened concrete as specified by the designer.
#HIGH STRENGTH CONCRETE MIX DESIGN CALCULATOR HOW TO#
HOW to Design High-Strength Concrete Mixture? (Note that high strength concrete does not guarantee durable concrete.) Some of these applications include dams, grandstand roofs, marine foundations, parking garages, and heavy duty industrial floors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
